Becky MortonPolitical reporter

 BBC
BBC
The government is looking at the possibility of cutting the rate of VAT on energy bills, Ed Miliband has suggested.
The energy secretary said he would not speculate ahead of the chancellor's Budget in November.
But asked if the government would consider scrapping the 5% rate, he told the BBC the country was facing a "cost-of-living crisis that we need to address as a government" and "we're looking at all of these issues".
The government is under pressure to reduce household energy costs and before the election Labour pledged to lower average bills by £300 a year by 2030.
Miliband told the BBC's Sunday with Laura Kuenssberg programme he stood by that promise but the reason bills were so high was "because of our dependence on fossil fuels".
He added: "There is only one route to get bills down, which is to go for clean power, home-grown, clean energy, that we control, so we're not at the behest of the petrol states and the dictators."
Pressed over whether the government was considering scrapping the 5% VAT rate on energy bills in November's Budget, Miliband said: "The whole of the government, including the chancellor, understand that we face an affordability crisis in this country.
"We face a cost-of-living crisis, a longstanding cost-of-living crisis, that we need to address as a government. We also face difficult fiscal circumstances... so obviously we're looking at all of these issues."
Scrapping VAT on domestic energy bills would save the average household £86 per year and cost an estimated £2.5bn per year to implement, according to the charity Nesta.
There was a rapid spike in energy prices in 2021, following Russia's invasion of Ukraine, and although costs have gone down, they have remained high by historical standards.
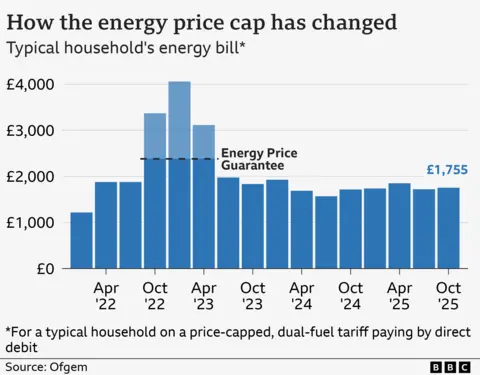
This month bills went up by 2% for millions of households, under the energy regulator Ofgem's price cap.
It means a household using a typical amount of energy will pay £1,755 a year, up £35 a year on the previous cap.

Earlier this week Chancellor Rachel Reeves told the BBC she was planning "targeted action to deal with cost-of-living challenges" in her Budget next month.
The BBC understands this could also include reducing some of the regulatory levies currently added to energy bills.
Levies known as "policy costs" - which are used to fund environmental and social schemes such as subsidies for renewables - made up around 16% of the average electricity bill and 6% of the average gas bill last year.
Some energy bosses have argued green levies are partly to blame for rising bills and the government's independent adviser, the Climate Change Committee, has long recommended removing policy costs from electricity bills to help people feel the benefits of net-zero transition.
Asked whether these could be funded through taxes rather than coming off energy bills, Miliband said: "That's always a judgement for the chancellor, but let's be honest we know we've got really difficult fiscal circumstances that we inherited... but absolutely we look at those things."
He argued the government had to invest in "aging electricity infrastructure" but there needed to be a "balance between public expenditure and levies".
The cost of household energy bills has become a major political battleground, with the Conservatives and Reform UK blaming net-zero policies for higher prices.
The Conservatives have said they would scrap the Climate Change Act, which legally requires the UK government to reduce emissions to net zero by 2050, as well as ditch carbon taxes on electricity generation and cut a funding scheme for renewables.
Shadow energy secretary Claire Coutinho said her party's plans would cut electricity bills for everyone by 20%.
"[The public] care about climate change but what I don't think they are signing up for is much higher bills and jobs being lost to countries abroad," she told the BBC.
In an interview with the same programme, Green Party leader Zack Polanski argued nationalising energy companies would help cut costs for customers.
His party has also proposed a new tax on carbon emissions to drive fossil fuels out of the economy and raise money to invest in the green transition.
Challenged over whether businesses would simply pass on these costs to customers, Polanski rejected this and said the tax would be "vital for tackling the climate crisis".
"What we need to be doing is finding other ways to support particularly small and local businesses... We know the big corporations are destroying our environment, our democracy and our communities," he said.
"They can make a profit, sure, but this isn't about squeezing out every single profit they can make."



 3 months ago
79
3 months ago
79